43. Convolution in Self-Driving Cars
Nd113 C7 40 L Convolution In Self-Driving Cars
Frequency in images
We have an intuition of what frequency means when it comes to sound. High-frequency is a high pitched noise, like a bird chirp or violin. And low frequency sounds are low pitch, like a deep voice or a bass drum. For sound, frequency actually refers to how fast a sound wave is oscillating; oscillations are usually measured in cycles/s (Hz), and high pitches and made by high-frequency waves. Examples of low and high-frequency sound waves are pictured below. On the y-axis is amplitude, which is a measure of sound pressure that corresponds to the perceived loudness of a sound and on the x-axis is time.
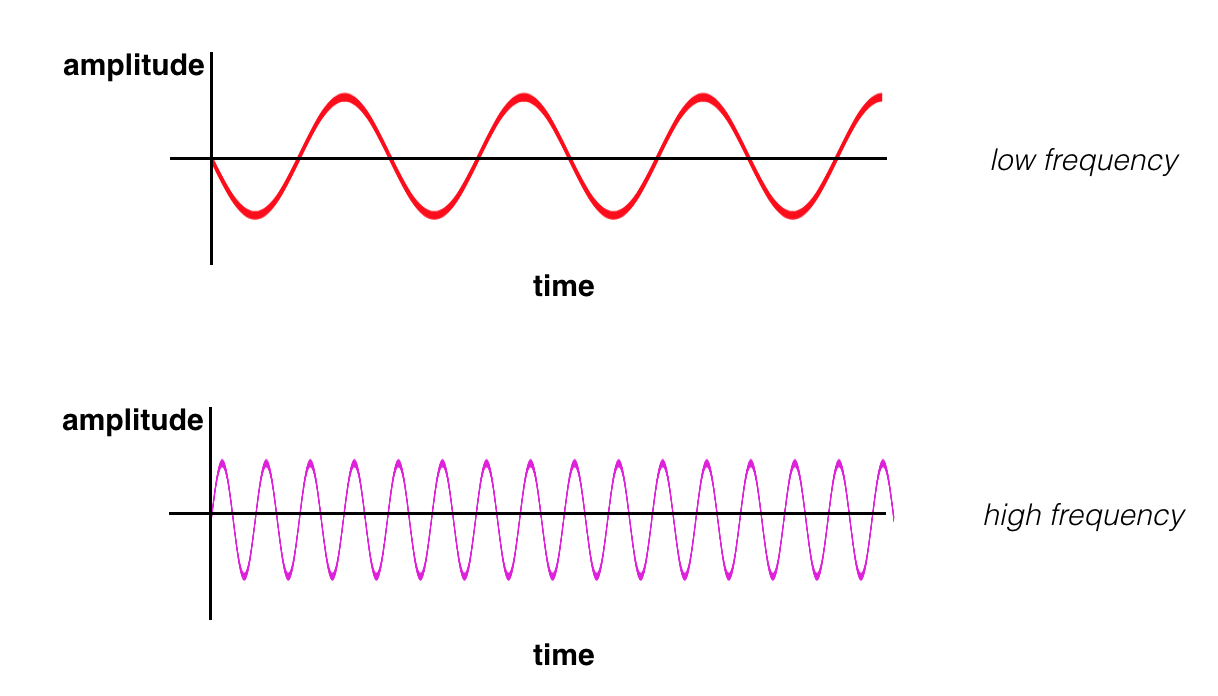
(Top image) a low frequency sound wave (bottom) a high frequency sound wave.
High and low frequency
Similarly, frequency in images is a rate of change. But, what does it means for an image to change? Well, images change in space, and a high frequency image is one where the intensity changes a lot. And the level of brightness changes quickly from one pixel to the next. A low frequency image may be one that is relatively uniform in brightness or changes very slowly. This is easiest to see in an example.
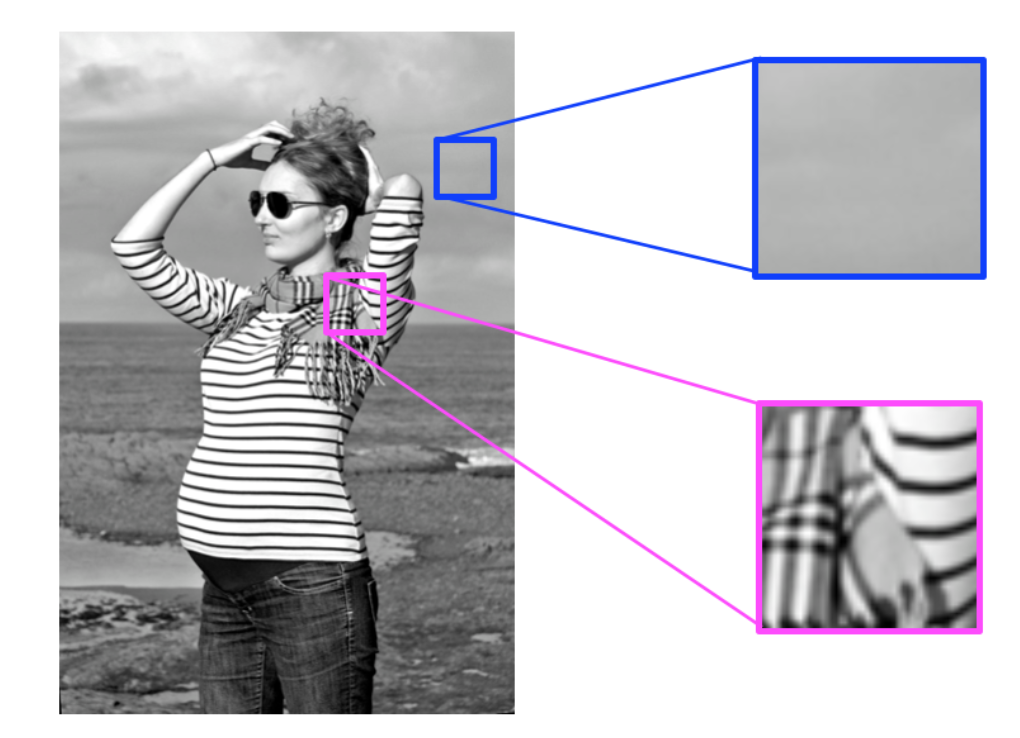
High and low frequency image patterns.
Most images have both high-frequency and low-frequency components. In the image above, on the scarf and striped shirt, we have a high-frequency image pattern; this part changes very rapidly from one brightness to another. Higher up in this same image, we see parts of the sky and background that change very gradually, which is considered a smooth, low-frequency pattern.
High-frequency components also correspond to the edges of objects in images, which can help us classify those objects.
Please see this reference for information on the Roberts Cross operators.